Introduction:
Vertical farming with hydroponics has gained significant popularity, particularly in urban areas facing space constraints. This innovative agricultural practice allows for the efficient cultivation of crops in vertically stacked layers, overcoming the limitations of traditional farming methods. Vertical farming maximizes land utilization and offers year-round crop production independent of external weather conditions by utilizing controlled environments, LED lighting, and precise nutrient delivery systems. It provides a sustainable solution for local food production, reducing the need for long-distance transportation and minimizing environmental impact. With advancements in technology and increased adoption, vertical farming has the potential to revolutionize agriculture and contribute to food security in urban environments.
What is Vertical farming?
Vertical farming is an advanced agricultural technique that optimizes space utilization by cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers or structures. This innovative approach involves creating controlled environments, utilizing LED lighting, and implementing precise nutrient delivery systems. Hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics are employed instead of traditional soil-based cultivation methods. Vertical farming enables year-round crop production, regardless of external weather conditions, and significantly reduces water consumption compared to conventional farming practices.
The benefits of vertical farming include the following:
- Increased crop yields.
- Reduced reliance on pesticides and herbicides.
- The ability to establish agricultural operations in urban areas.
Although there are initial setup costs and energy requirements associated with vertical farming systems, this sustainable approach offers the potential for localized and fresh food production while minimizing the environmental impact of traditional farming. With ongoing technological advancements and the growing demand for sustainable agriculture, vertical farming holds promise for addressing food security challenges in densely populated regions.
Techniques Utilized in Vertical Farming: Enhancing Agricultural Efficiency:
Vertical farming, a cutting-edge agricultural method, incorporates various techniques to maximize space utilization and optimize crop production in vertically stacked structures. These techniques revolutionize traditional farming practices, enabling year-round cultivation and reducing the environmental impact.
One well-known technique employed in vertical farming is hydroponics, which eliminates the need for soil and utilizes a water-based nutrient solution. This method allows plants to grow directly in water, providing precise control over nutrient delivery and minimizing water usage. Another technique is aeroponics, where plants are grown in an air or mist environment with nutrient-rich water sprayed onto their roots. This technique promotes accelerated growth and efficient nutrient absorption.
Aquaponics combines fish farming with hydroponics, creating a mutually beneficial system. The plants receive nutrients from the fish waste and filter and clean the fish’s water.
Furthermore, vertical farming relies on advanced technologies such as LED lighting systems, which provide the necessary light spectrum for optimal plant growth. Controlled environments with precise temperature, humidity, and airflow control ensure optimal growing conditions, irrespective of external weather factors.
These techniques employed in vertical farming enhance agricultural efficiency, allowing for increased crop yields, reduced water consumption, and minimized reliance on chemical pesticides and herbicides. By overcoming space limitations and utilizing sustainable farming practices, vertical farming can revolutionize agriculture and contribute to food security in urban areas.
Hydroponics – Revolutionary Soilless Cultivation:
Hydroponics is a groundbreaking technique employed in vertical farming that revolutionizes traditional soil-based cultivation practices. In this soilless system, plants are grown in nutrient-rich water solutions, allowing precise control over their growth and development.
In hydroponics, plants are typically placed in containers or troughs with their roots directly immersed in the nutrient solution. The solution contains all the necessary minerals and nutrients required for plant growth. Hydroponics by delivering nutrients to the roots eliminates the need for soil, providing several advantages.
Moreover, hydroponics enables year-round crop production, independent of seasonal changes or weather conditions. By providing a controlled environment with optimal temperature, humidity, and lighting, hydroponic systems create ideal growing conditions for plants.
Steps in hydroponics:
Hydroponics is crucial in maximizing space utilization in vertical farming, as plants can be grown vertically in stacked layers. This method allows for cultivating more plants in a smaller footprint, making it particularly suitable for urban agriculture.
Firstly, hydroponics optimizes resource utilization, including water. Compared to traditional farming, hydroponic systems use significantly less water, as it is recirculated and reused within the system. This water efficiency is crucial in water-scarce regions and contributes to sustainable agriculture.
Secondly, hydroponics allows for precise control over nutrient delivery, ensuring that plants receive the optimal balance of essential elements required for their growth. This accurate control promotes faster growth rates, healthier plants, and higher crop yields than conventional farming methods.
Additionally, hydroponics eliminates the risks associated with soil-borne diseases and pests, as plants are grown in a sterile environment. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides, making hydroponics an environmentally friendly and sustainable cultivation method.
Types of Solutions Used in Hydroponics in Nurturing Plant Growth:
In hydroponics, various types of nutrient solutions are used to provide essential elements required for plant growth and development. These solutions substitute for soil, delivering a balanced mix of nutrients directly to the plant roots. Here are the different types of solutions commonly used in hydroponic systems:
- Complete Nutrient Solutions: These solutions contain a broad mix of essential nutrients, including micronutrients, such as iron, zinc, and copper, and macronutrients, like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. They provide a well-rounded nutrient profile to support overall plant growth.
- Customized Nutrient Solutions: Depending on the specific needs of different plant species, customized nutrient solutions can be formulated. By adjusting the ratios and concentrations of individual nutrients, these solutions ensure optimal nutrition tailored to the requirements of specific crops.
- pH-Adjusted Solutions: pH plays a crucial role in nutrient absorption and plant availability. pH-adjusted solutions are formulated to maintain the appropriate pH level for optimal nutrient uptake. Acidic or alkaline solutions can modify the pH, ensuring plants can absorb nutrients effectively.
- Organic Nutrient Solutions: Organic nutrient solutions are available for growers who prefer organic farming. These solutions are derived from natural sources, such as compost, seaweed extracts, or organic minerals. They provide an organic alternative for nutrient supplementation in hydroponics.
Hydroponic systems can provide the optimal conditions for plants to thrive and produce high-quality crops by carefully monitoring and adjusting nutrient solutions. Each solution delivers essential nutrients to plants, supporting their growth and productivity. The right solution is chosen based on the preferences of the growers as well as the needs of the plants being grown.
Real-World Example of Hydroponic Solutions in Vertical Farming:
These examples highlight hydroponic solutions’ diverse applications and success in vertical farming. They showcase how this technology is revolutionizing agriculture by enabling the cultivation of fresh, nutritious produce in urban areas, reducing the environmental impact, and creating more sustainable food systems.
A pioneering vertical farm that utilizes hydroponic systems to grow leafy greens sustainably and efficiently, multiple vertical towers are employed, each containing various tiers of growing trays. These trays are filled with a specialized hydroponic solution that provides the necessary nutrients for plant growth. The nutrient-rich solution is continuously circulated, ensuring plants receive a constant supply of essential elements.
A leading urban agriculture company with multiple hydroponic greenhouses across the United States specializing in growing high-quality, pesticide-free greens and herbs using advanced hydroponic systems. Their vertical farming approach maximizes space utilization and reduces environmental impact while supplying fresh produce to local communities.
An innovative vertical farming company utilizes hydroponic systems to grow various crops, including leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries. They operate large-scale indoor farms with advanced technology to optimize plant growth and ensure consistent quality. Their hydroponic solutions enable them to produce food closer to consumers, minimizing transportation and reducing the carbon footprint associated with traditional farming methods.
One urban vertical farm in New York City that specializes in growing rare and exotic herbs, microgreens, and edible flowers employs hydroponics to cultivate its crops in a controlled environment. Hydroponic solutions can precisely tailor nutrient delivery and environmental conditions to each plant’s needs, producing high-quality, flavorful produce.
Cost, Efficiency, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Hydroponic Solutions:
Hydroponic solutions in vertical farming offer several benefits but also come with specific considerations. Let’s explore the cost, efficiency, advantages, and disadvantages of utilizing hydroponic solutions:
- Cost: Hydroponic systems often require an initial investment for equipment, infrastructure, and maintenance. However, long-term operational costs can be reduced due to efficient water usage, minimized fertilizer requirements, and potential higher crop yields.
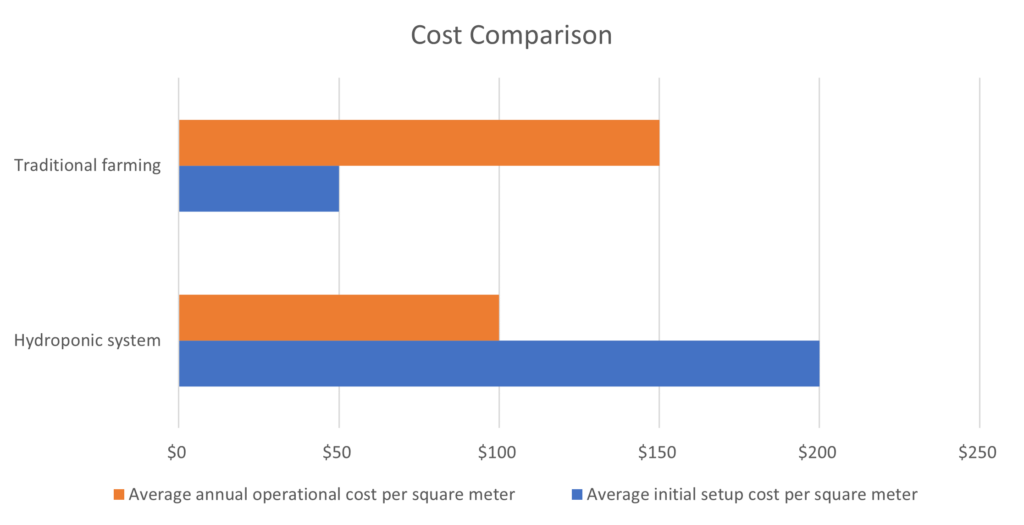
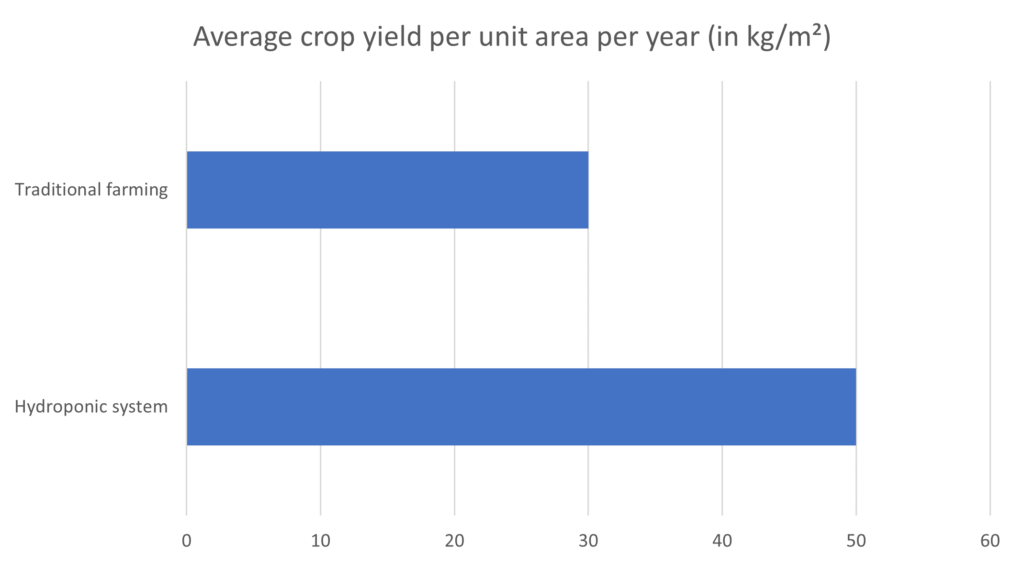
- Efficiency: Hydroponic solutions provide better control over growing conditions, leading to higher crop yields and faster growth rates than traditional farming methods. The precise delivery of nutrients and water directly to plant roots optimizes resource utilization and minimizes waste.
Advantages:
- Conserve water: Hydroponic systems use up to 90% less water than conventional farming, making them more water-efficient and environmentally friendly.
- Maximizes space utilization: Vertical farming with hydroponics allows for high-density crop cultivation, efficiently using limited urban spaces.
- Year-round production: Controlled indoor environments enable crop cultivation, reducing reliance on seasonal variations.
Disadvantages:
- Initial setup costs: The initial investment for hydroponic systems can be higher than traditional farming methods.
- Technical expertise: Hydroponic farming requires specialized knowledge and skills for system setup, nutrient management, and troubleshooting.
- Reliance on technology: Dependence on technology and equipment for precise control and monitoring increases vulnerability to power outages or system failures.
By analyzing the graph data, we can visually compare hydroponic solutions’ cost and yield efficiency against traditional farming methods, providing valuable insights into hydroponics’ economic viability and productivity in vertical farming.
Comparison between Regular Farming Practices and Hydroponic Vertical Farming Practices:
Regular farming practices involve cultivating crops in soil using traditional methods, relying on natural sunlight and rainfall. It typically requires large land areas and is dependent on weather conditions, making it susceptible to variations in crop yields. Water usage can be inefficient, and nutrient management may be challenging, leading to potential nutrient deficiencies or excesses. Pests and diseases can also pose significant challenges, requiring pesticides and other control measures.
On the other hand, hydroponic vertical farming practices utilize soilless systems and controlled environments. This method allows for year-round cultivation, irrespective of seasonal changes, making it suitable for urban areas with limited space. Water and nutrient delivery in hydroponics are optimized, reducing water consumption and precise nutrient management, leading to healthier and more productive crops. Pest and disease control can be more effectively managed in a controlled environment, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
When comparing the two approaches, hydroponic vertical farming offers several advantages. It maximizes space utilization by growing crops vertically, making it ideal for urban settings with limited land availability. It also enhances resource efficiency by conserving water and minimizing fertilizer through precise nutrient delivery. Additionally, hydroponics enables consistent crop yields throughout the year, unaffected by seasonal variations.
While hydroponic vertical farming has advantages, there are also some considerations. The initial setup cost of hydroponic systems can be higher than traditional agriculture, requiring investment in infrastructure and equipment. Vertical farming’s artificial lighting and climate control can also increase energy consumption.
Here’s a tabular representation comparing Regular Farming Practices and Hydroponic Vertical Farming Practices:
| Regular Farming Practices | Hydroponic Vertical Farming Practices | |
| Space Utilization | Requires large land areas | Maximizes space utilization, suitable for urban areas with limited space |
| Resource Efficiency | Water usage can be inefficient | Subject to seasonal variations, crop losses are possible |
| Crop Yields | Optimizes water and nutrient delivery, and reduces water consumption and fertilizer use. | Consistent crop yields throughout the year |
| Pest and Disease Control | Relies on pesticides and control measures | Optimizes water and nutrient delivery and reduces water consumption and fertilizer use. |
| Setup Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial setup cost for infrastructure and equipment |
| Energy Consumption | Relies on natural sunlight and rainfall | Artificial lighting and climate control may increase energy consumption |
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hydroponic vertical farming presents a compelling solution for sustainable and efficient food production, especially in urban areas with limited space. It offers significant advantages such as maximized space utilization, resource efficiency, and consistent yearly crop yields. Hydroponics reduces water consumption and minimizes fertilizer use by optimizing water and nutrient delivery, contributing to environmental sustainability. Although there may be higher initial setup costs and increased energy consumption in artificial lighting and climate control, the long-term benefits outweigh these challenges. As urbanization and the demand for food continue to rise, vertical hydroponic farming holds great potential to ensure a resilient and productive agricultural future.



