Introduction:
The advent of autonomous tractors equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) and GPS technology has brought significant advancements to the agricultural sector. These intelligent machines have the potential to transform farming practices, offering numerous benefits such as increased efficiency, improved productivity, and optimized resource management.
Benefits of Autonomous Tractors:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Autonomous tractors can operate continuously without human intervention, minimizing downtime and increasing overall productivity. They can work around the clock, optimizing field operations and reducing labor requirements.
- Precision Farming: With the integration of AI and GPS, autonomous tractors offer precise navigation and positioning, resulting in accurate seed placement, optimized fertilizer application, and targeted pest control. This precision farming approach improves crop yield, minimizes waste, and enhances resource utilization.
- Time and Cost Savings: Autonomous tractors can perform tasks efficiently and autonomously, saving time and reducing labor costs. They can navigate fields, monitor crop health, and execute operations with minimal human intervention, freeing up valuable time for farmers to focus on other critical aspects of their operations.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Autonomous tractors generate vast amounts of data on soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns. These data are analyzed by AI algorithms, which offer useful information that helps farmers decide on irrigation, fertilization, and pest management strategies. This data-driven approach optimizes farming practices and improves overall farm management.
Technology Behind Autonomous Tractors:
Artificial intelligence (AI) and Global Positioning System (GPS) technology are crucial in enabling the autonomy of tractors in modern agriculture. Here is a detailed description of the role of AI and GPS in autonomous tractors:
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI algorithms enable autonomous tractors to process data, make decisions, and execute tasks based on real-time information. Machine learning and computer vision technologies are crucial in analyzing data, identifying patterns, and adapting tractor operations for optimal performance.
- Perception and Sensing: AI algorithms are used to analyze data from various sensors on the tractor, such as cameras, LiDAR, and radar, to perceive and understand the environment. This allows the tractor to detect obstacles, identify crops, and make real-time decisions based on the data received.
- Decision-Making: AI algorithms process the sensor data and make intelligent decisions regarding path planning, navigation, and task execution. The AI system considers field boundaries, optimal routes, and potential hazards to ensure safe and efficient tractor operations.
- Machine Learning: AI-based machine learning techniques enable the tractor to learn and adapt over time. By analyzing historical data and farmer input, autonomous tractors can improve their performance, optimize resource usage, and enhance decision-making in different farming scenarios.
Global Positioning System (GPS):
GPS technology provides precise location information, allowing autonomous tractors to navigate fields accurately. GPS-based guidance systems enable path planning, reducing overlaps and ensuring efficient coverage during seeding, spraying, and harvesting operations.
- Positioning and Localization: GPS technology provides accurate positioning information to the autonomous tractor, allowing it to know its exact location within the field. This information is crucial for precise navigation, field mapping, and implementing accurate farming practices.
- Geofencing and Boundaries: GPS enables the creation of virtual boundaries, known as geofences, within which the tractor can operate. This helps ensure the tractor stays within the designated area and avoids unauthorized or sensitive regions.
- Route Planning and Guidance: GPS data is used for route planning, allowing the tractor to navigate efficiently between different field areas. GPS guidance systems provide real-time feedback to the tractor, ensuring it follows the designated paths and rows accurately.
Combining AI and GPS technology in autonomous tractors empowers them to operate independently and perform tasks precisely and efficiently. AI enables the tractor to perceive and interpret the environment, make intelligent decisions, and learn from past experiences. GPS technology provides accurate positioning, helps geofencing, and guides the tractor along designated routes. AI and GPS revolutionize farming practices by enhancing productivity, reducing labor requirements, and optimizing resource usage.
Real-Time Applications:
- Seeding and Planting: Autonomous tractors can accurately sow seeds at optimized depths and intervals, ensuring uniform crop emergence and minimizing seed wastage.
- Crop Monitoring and Health Assessment: By collecting and analyzing data on crop health, autonomous tractors can detect early signs of stress, disease, or nutrient deficiencies. This enables farmers to take timely corrective measures, leading to improved crop quality and yield.
- Precision Spraying: Autonomous tractors equipped with intelligent spraying systems can precisely apply fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides based on crop needs, reducing chemical usage and minimizing environmental impact.
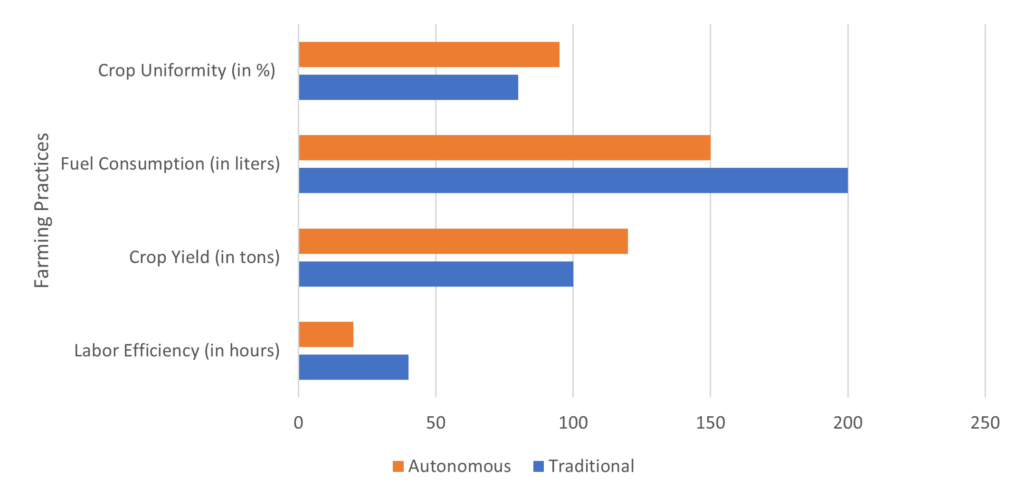
Comparison between Traditional and Autonomous Farming Practices:
The adoption of autonomous tractors revolutionizes farming practices in several ways:
- Labor Efficiency: Autonomous tractors reduce the need for manual labor, leading to significant labor savings and increased operational efficiency.
- Precision and Accuracy: Autonomous tractors offer precise navigation, targeted operations, and data-driven decision-making, resulting in improved accuracy, reduced waste, and optimized resource utilization.
- Time Savings: Autonomous tractors can operate continuously, performing tasks efficiently and autonomously, saving valuable time for farmers.
- Scalability: Autonomous tractors enable scalability and the ability to easily manage larger farm areas, allowing farmers to expand their operations.
Implementations and Results:
Various farms and agricultural companies have embraced autonomous tractors, reporting positive outcomes. Implementations have shown improved crop yields, reduced labor costs, enhanced operational efficiency, and improved resource management. Case studies and field trials have demonstrated autonomous tractors’ effectiveness and economic benefits across different crops and farming systems.
For example, a university utilized autonomous tractors for the entire crop cycle of a hectare of land. The autonomous tractor performed tasks such as soil preparation, sowing, crop monitoring, and harvesting without human intervention.
Another leading agricultural equipment manufacturer offers the AutoTrac system that enables autonomous steering for their tractors. Farmers using AutoTrac have reported increased precision in field operations, reducing overlap and improving overall efficiency. The system has been shown to reduce operator fatigue, allowing them to focus on other tasks and improving productivity.
Advantages:
- Increased operational efficiency and productivity.
- Optimized resource utilization and reduced waste
- Improved precision and accuracy in farming operations
- Data-driven decision-making for optimized crop management
- Time and labor savings
Disadvantages:
- High initial investment and implementation costs
- Technical complexities and potential for technical issues
- Dependence on reliable GPS signals and connectivity
- Requirement for training and skill development for operating and maintaining autonomous tractors.
Conclusion:
Autonomous tractors with artificial intelligence and GPS technology are revolutionizing modern farming practices. With their ability to operate autonomously, analyze data, and optimize farming operations, these tractors offer numerous benefits to farmers. Despite specific challenges, the advantages of adopting autonomous tractors, including increased efficiency, improved productivity, and optimized resource management, make them valuable tools in modern agriculture. As technology advances, the potential for further enhancements in autonomous tractor capabilities and their widespread adoption in the farming industry is promising.



