Introduction:
Global food security is significantly threatened by climate change, necessitating climate-smart agriculture (CSA) techniques. However, selecting the most appropriate CSA technologies for a specific context can be complex and challenging. This article introduces the Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool, which provides a systematic and participatory approach to prioritize context-specific CSA technologies. The CSA-RA tool aims to assist stakeholders in making informed decisions by considering various factors, including climate resilience, productivity, resource efficiency, and socio-economic aspects. Using the CSA-RA tool, stakeholders can effectively identify and prioritize technologies that align with their needs, goals, and constraints. The tool enhances the efficiency of decision-making processes, ensuring that interventions are contextually relevant and maximizes the potential for climate resilience and sustainability.
Climate Smart Agriculture:
Climate Smart Agriculture (CSA) is an approach that aims to effectively transform agricultural systems to address the challenges posed by climate change. It involves implementing sustainable and resilient practices that enhance productivity, adapt to changing climate conditions, and mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. By integrating scientific knowledge, technology, and local knowledge, CSA seeks to optimize resource use, minimize environmental impacts, and improve the livelihoods of farmers and communities.
The fundamental principles of CSA include,
- increasing agricultural productivity,
- enhancing resilience and adaptation to climate change,
- reducing emissions of farm activities, and
- promoting sustainable resource management.
CSA contributes to food security, poverty reduction, and environmental sustainability by adopting climate-smart practices and strategies, such as conservation agriculture, precision farming, agroforestry, and efficient water management.
Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) Tool:
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) Tool is a valuable resource for prioritizing context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. This tool is designed to assist stakeholders, researchers, and policymakers in identifying and selecting the most appropriate climate-smart agricultural practices and technologies for a given agrarian context. The CSA-RA Tool follows a systematic approach, combining scientific knowledge, data collection, and stakeholder engagement to evaluate and assess the potential impacts, feasibility, and suitability of different climate-smart agriculture interventions.
By considering multiple criteria, such as environmental sustainability, economic viability, social acceptability, and climate resilience, the CSA-RA Tool helps prioritize and guide decision-making processes. It allows users to assess the effectiveness and potential risks of different technologies, enabling the identification of practical and locally relevant solutions to climate change challenges. The CSA-RA Tool ultimately aims to support the implementation of climate-smart agriculture strategies that enhance agricultural productivity, promote adaptation to climate change, and contribute to sustainable development.
Methodology and Steps Involved:
The methodology and steps involved in the Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool provide a structured and systematic approach to assess and prioritize context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. The methodology encompasses a series of critical steps that guide the implementation of the CSA-RA tool.
These steps typically include the following:
- Planning: Defining the objectives, scope, and context of the assessment, identifying stakeholders, and forming an assessment team.
- Data Collection: Gather relevant information on the agricultural system, climate conditions, existing technologies, and local socio-economic factors.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving key stakeholders, such as farmers, researchers, policymakers, and extension agents, in the assessment process to ensure diverse perspectives and local knowledge are considered.
- Criteria Selection: Identifying and defining criteria that will be used to evaluate and prioritize climate-smart agriculture technologies. These criteria may include climate resilience, environmental sustainability, economic viability, and social acceptability.
- Technology Evaluation: Assessing the potential impacts, benefits, risks, and constraints associated with different climate-smart agriculture technologies based on the selected criteria.
- Prioritization: Using a structured approach, ranking and prioritizing the identified technologies based on their overall performance and suitability in the specific context.
- Recommendations and Decision-making: Providing recommendations and insights to support decision-making processes, such as selecting the most appropriate technologies for implementation and designing strategies to promote their adoption and scaling up.
The methodology and steps involved in the CSA-RA tool ensure a comprehensive and rigorous assessment of climate-smart agriculture technologies, facilitating evidence-based decision-making and fostering the adoption of sustainable and context-specific practices.
Explanation of Technologies Used in the Tool:
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool incorporates various technologies to assess and prioritize context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. These technologies are instrumental in gathering data, analyzing information, and generating insights for decision-making.
The CSA-RA tool makes use of several critical technologies, including:
- Geographic Information System (GIS): GIS technology enables the mapping and visualization of spatial data, such as climate patterns, soil characteristics, and land use. It helps identify suitable areas for implementing climate-smart agriculture technologies and assessing their potential impacts.
- Remote Sensing: In remote sensing, changes in vegetation, land cover, and other environmental factors are tracked and analyzed using satellite imagery and aerial photography. It provides valuable information for assessing the suitability and effectiveness of different climate-smart agriculture technologies.
- Data Analytics: Data analytics tools and techniques are employed to process and analyze large datasets, including climate data, agricultural production data, and socio-economic indicators. These tools enable the identification of trends, patterns, and correlations, facilitating evidence-based decision-making.
- Decision Support Systems (DSS): DSS tools provide a structured framework for evaluating and comparing different climate-smart agriculture technologies. They integrate data, models, and algorithms to generate recommendations and insights for decision-making.
- Mobile Data Collection: Mobile-based data collection tools allow for the efficient collection of field-level data, including farmer feedback, technology adoption rates, and performance indicators. These tools streamline the data collection process, ensuring accuracy and timeliness.
- Stakeholder Engagement Platforms: Online platforms and applications facilitate stakeholder engagement and participation in the CSA-RA process. These platforms enable knowledge sharing, collaboration, and feedback from farmers, researchers, policymakers, and other stakeholders.
Incorporating these technologies in the CSA-RA tool enhances its effectiveness and efficiency in assessing and prioritizing climate-smart agriculture technologies. They enable data-driven decision-making, improve monitoring and evaluation processes, and promote adopting sustainable agricultural practices.
Implementations and Results:
The performance of the Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool has yielded significant results in various regions around the world. Several real-world examples showcase the tool’s effectiveness in prioritizing and implementing context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies.
In a farming community in Sub-Saharan Africa, the CSA-RA tool was employed to assess the suitability of different climate-smart agriculture technologies. Farmers adopted improved irrigation techniques and agroforestry practices based on the tool’s recommendations. As a result, crop yields increased, water use efficiency improved, and soil health was enhanced.
In a coastal region vulnerable to climate change impacts, the CSA-RA tool was utilized to identify climate-smart agriculture technologies that mitigate the risk of saline intrusion. Through the tool’s assessment, farmers implemented salt-tolerant crop varieties and improved water management practices. This led to reduced crop losses and increased resilience to saltwater intrusion.
In a mountainous region prone to soil erosion, the CSA-RA tool guided the implementation of conservation agriculture practices, such as contour plowing and agroforestry systems. These practices helped prevent soil erosion, enhance water retention, and improve farm productivity.
The CSA-RA tool was employed in a large-scale commercial farming operation to prioritize climate-smart agriculture technologies. Based on the tool’s analysis, the farm implemented precision farming techniques, including variable rate fertilizer application and yield monitoring. This resulted in optimized resource use, reduced environmental impact, and improved economic returns.
These real-world examples demonstrate the practical application and positive outcomes of using the CSA-RA tool. By tailoring climate-smart agriculture technologies to specific contexts, the tool assists farmers in making informed decisions and implementing sustainable practices that enhance productivity, resilience, and environmental stewardship.
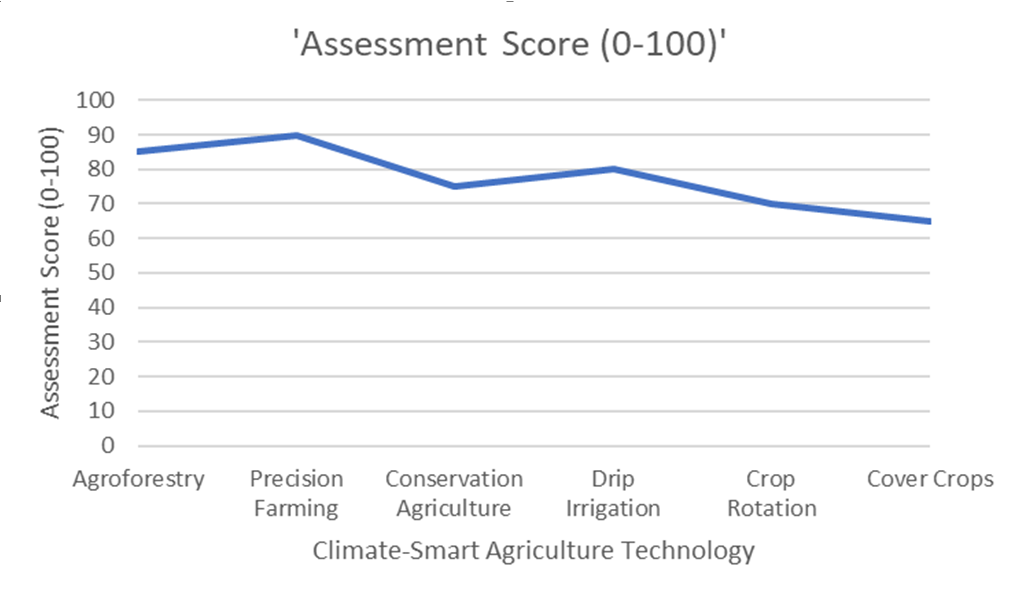
Advantages and Disadvantages:
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool offers several advantages in prioritizing context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. However, it also comes with certain limitations. Here are the key advantages and disadvantages associated with the CSA-RA tool:
Advantages:
- Enhanced decision-making: The CSA-RA tool systematically prioritizes climate-smart agriculture technologies, enabling farmers and stakeholders to make informed decisions based on scientific assessments and data.
- Tailored solutions: By considering the specific context of a region or farm, the tool helps identify technologies well-suited to local conditions, leading to more effective and context-specific climate-smart solutions.
- Resource optimization: The tool enables the efficient allocation of resources by prioritizing technologies with the most significant potential to address climate change challenges, thereby maximizing the benefits and minimizing waste.
- Increased resilience: Farmers can increase their resistance to climate change impacts like extreme weather events, water scarcity, and soil degradation by choosing climate-smart agriculture solutions through the CSA-RA tool.
Disadvantages:
- Data requirements: The CSA-RA tool relies on accurate and up-to-date data on climate, soil, and other relevant factors. Acquiring such data may pose challenges, especially in data-scarce regions or for small-scale farmers with limited resources.
- Subjectivity: Despite its systematic approach, the tool’s assessments may still involve subjective judgment and interpretation, which could introduce bias or variation in the results.
- Complexity: The CSA-RA tool may require technical expertise and training to implement and interpret its results effectively. This could limit its accessibility to farmers with limited technical knowledge or resources.
- Scalability: While the tool has proven effective in various case studies, its scalability and applicability to different regions and farm sizes may vary. Adapting the tool to diverse contexts may require customization and additional research.
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of the CSA-RA tool is crucial for its successful application. By leveraging its strengths and addressing its limitations, stakeholders can optimize the tool’s utility in prioritizing and implementing climate-smart agriculture technologies.
Efficiency and Sustainability:
Efficiency and sustainability are critical considerations when utilizing the Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool.
In terms of efficiency, the tool assists in prioritizing climate-smart agriculture technologies that optimize resource utilization, including land, water, fertilizers, and energy. By identifying efficient practices, the tool facilitates higher agricultural productivity while minimizing resource waste. Additionally, the CSA-RA tool streamlines the decision-making process by providing a systematic and structured approach, saving time and effort for stakeholders. It enables targeted interventions by assessing a region or farm’s needs and constraints, resulting in more efficient climate-smart agriculture implementation.
Regarding sustainability, the CSA-RA tool considers the environmental impacts of selected technologies. It emphasizes practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, conserve water resources, promote biodiversity, protect soil health, and foster long-term environmental sustainability in agricultural systems. Moreover, the tool enables practices that enhance the resilience of farming systems to climate change, contributing to their long-term sustainability. Economic viability is also considered, as the tool aims to identify technologies that provide financial benefits to farmers, such as increased yields, cost savings, market opportunities, and improved livelihoods.
Efficiency and sustainability are interconnected in the context of climate-smart agriculture. The CSA-RA tool facilitates optimized resource utilization, streamlined decision-making, and adopting of environmentally sound, resilient, and economically viable practices. By prioritizing efficient and sustainable technologies, stakeholders can contribute to climate-smart agriculture initiatives’ long-term success and impact.
Conclusion:
The Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool is a valuable resource for stakeholders involved in climate-smart agriculture. The tool’s systematic and participatory approach supports decision-making processes by prioritizing context-specific CSA technologies. By considering multiple criteria and engaging stakeholders throughout the process, the CSA-RA tool enables the identification of appropriate interventions to enhance climate resilience, increase productivity, and promote sustainability in agriculture. The tool’s implementation in real-world examples demonstrates its effectiveness in guiding stakeholders toward climate-smart agricultural practices.
In conclusion, the Climate-Smart Agriculture Rapid Appraisal (CSA-RA) tool is valuable for prioritizing context-specific climate-smart agriculture technologies. It provides a systematic and structured approach to assessing the needs and constraints of agricultural systems, facilitating informed decision-making. Through the CSA-RA tool, stakeholders can identify and prioritize technologies that optimize resource utilization, enhance productivity, reduce environmental impacts, and promote resilience to climate change.
The tool’s methodology and steps guide users through a comprehensive assessment process, considering various factors such as climate, soil, water availability, and socio-economic conditions. It enables the evaluation of different technologies and their suitability for specific contexts, ensuring the adoption of solutions that address each farming system’s unique challenges and opportunities.
Implementations of the CSA-RA tool have shown promising results, with real-world examples demonstrating improved agricultural practices, increased yields, resource savings, and enhanced livelihoods for farmers. It is crucial to recognize that the instrument has drawbacks and difficulties, such as the requirement for ongoing monitoring and assessment, correct data availability, and stakeholder participation.
Overall, the CSA-RA tool is a valuable decision-support tool for promoting climate-smart agriculture. By prioritizing and implementing context-specific technologies, stakeholders can contribute to sustainable and resilient agricultural systems that effectively address the challenges of climate change while ensuring food security, environmental stewardship, and economic viability.



